Description
C. Difficile Toxin A & B Stool Test: Overview and Details
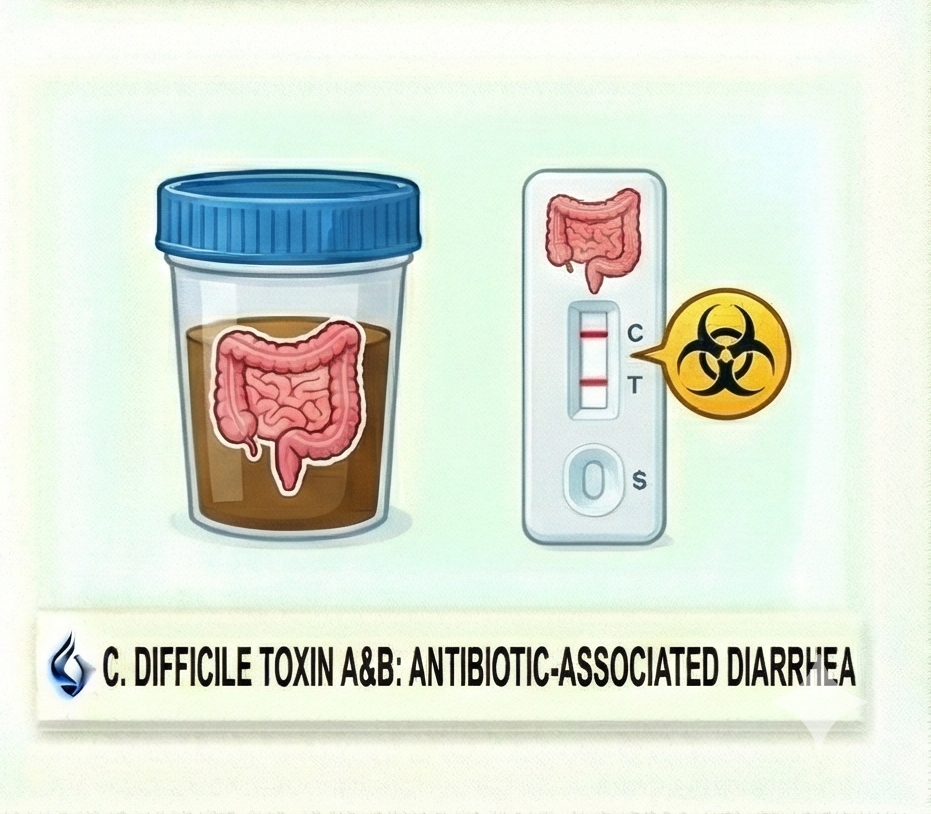
The C. Difficile Toxin A and B Stool Test (also known as Clostridioides difficile Toxins A and B EIA or similar assays) detects harmful toxins produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile (commonly called C. diff) in a stool sample. This test diagnoses active C. diff infection (CDI), a common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and severe colitis.

Why Is This Test Done?
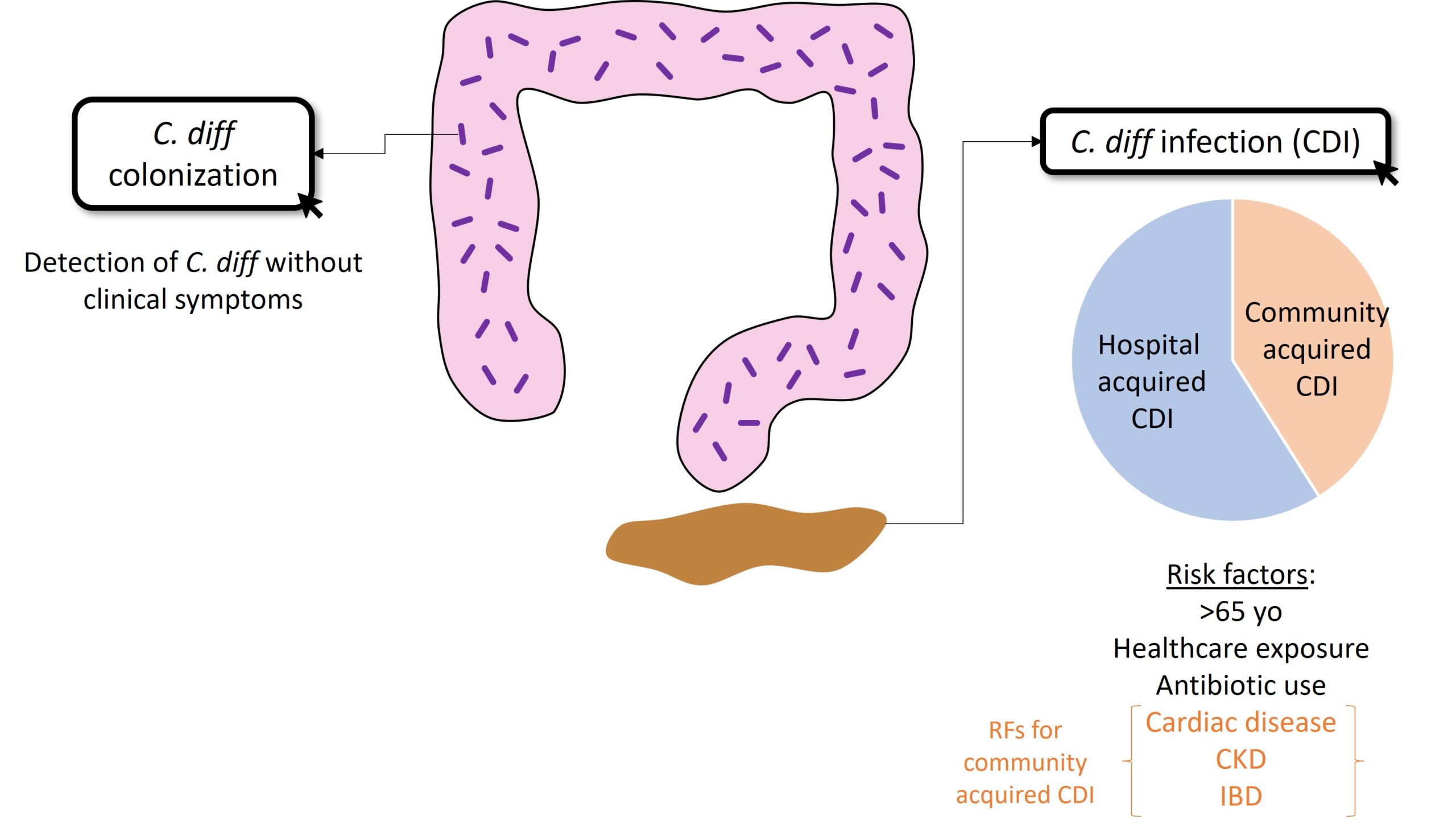
C. diff bacteria overgrow in the gut after antibiotic use disrupts normal flora. Pathogenic strains produce Toxin A (enterotoxin causing fluid secretion and inflammation) and Toxin B (cytotoxin damaging colon cells). The test identifies these toxins directly, confirming disease-causing infection (not just colonization).
Common reasons for testing:
- Persistent diarrhea (≥3 loose stools/day for ≥2 days)
- Recent antibiotic use or hospitalization
- Symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, or severe complications (e.g., pseudomembranous colitis)

How Is the Test Performed? (Procedure)
- Sample Collection: Provide a fresh, unformed/liquid stool sample in a clean, sterile container (avoid urine or water contamination). Use a stool collection kit if available.
- Transport: Deliver to the lab quickly (ideally within 2 hours) or refrigerate, as toxins degrade rapidly at room temperature.
- Lab Method: Use Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA) or similar to detect Toxins A and B. Some labs combine with GDH antigen screening or PCR for better accuracy.



Interpretation of Results
- Positive — Toxins A and/or B detected → Likely active C. diff infection → Start treatment (e.g., vancomycin or fidaxomicin).
- Negative — No toxins detected → Infection unlikely, but false negatives possible (sensitivity ~75-90%) → Consider repeat testing or alternatives if symptoms persist.
Labs often use multi-step algorithms (e.g., GDH + Toxin EIA, or PCR reflex) for higher accuracy.
Important Notes
- Test only unformed stools in symptomatic patients (avoid testing formed stools to prevent detecting harmless colonization).
- Not for children <2 years routinely, as carriage is common.
- Consult your doctor for personalized advice.
If you experience symptoms or need this test (code GD151 in some labs, MRP varies), contact your healthcare provider or local diagnostic center promptly. Early detection prevents complications!